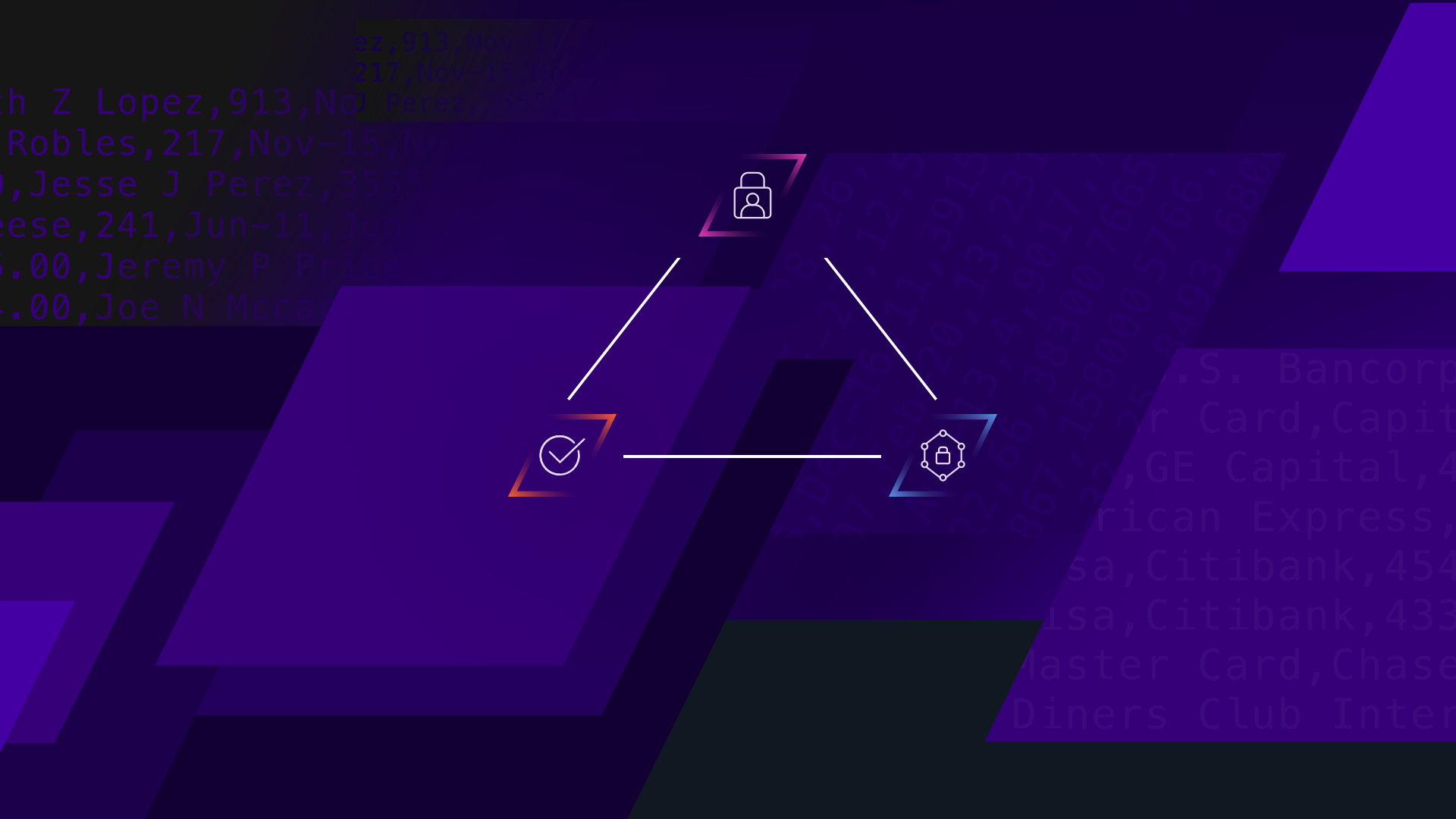
If you’re familiar with the cybersecurity world, you’ve probably heard of the CIA triad.
This concept breaks information security measures into three key components: confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
The CIA triad is particularly useful in guiding policies and developing frameworks for information security. It’s also the foundation for major governmental data regulations like the European Union’s GDPR.
- Confidentiality: the property of information not being available or disclosed to unauthorized users. Data can only be accessed by the intended individuals or entities.
- Integrity: the property of accuracy and completeness. Data cannot be modified by unauthorized users at any stage of its lifecycle or in transit.
- Availability: the property of accessibility and usability on demand. Data systems must function so that authorized users are able to access data whenever and wherever they need.
When was the CIA triad first introduced?
The concept of the CIA triad developed over time. Its ideas were first introduced in the 1972 Anderson Report, which discussed computer security for the Air Force’s Electronic System Division.
Over the next decade, cybersecurity would shift from a defense sector concern to a commercial industry concern. Banks, financial services, and other businesses would start to seek not only confidentiality but also integrity, since it was important that their electronic data remain unmodified by unauthorized users.
By the late 1980s, the first internet DoS attack would demonstrate the need for data availability. From there, the CIA abbreviation was born.
The CIA triad today
While some experts believe that cybersecurity will require a broader paradigm in the future, the CIA triad remains highly relevant today. With the growing threat of ransomware and other cyberattacks, it offers critical qualities to consider in data protection. As the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers put it, "Confidentiality, integrity and availability (CIA) are the very foundation of data protection and privacy.
Below, we’ll detail each of the three components of the CIA triad. We’ll also explain how ShardSecure upholds the CIA triad — and what that means for your data protection.
Data confidentiality
The first pillar of the CIA triad, data confidentiality keeps information private from viewing, sharing, use, and modification to prevent identity theft, legal problems, and other consequences. Some common examples of highly confidential data include:
- Social Security numbers
- Driver’s license and other ID numbers
- Credit card numbers
- Passwords
- Medical records
- Financial records
Luckily, laws and regulations exist to help protect confidential information. For instance, the Healthcare Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) prevents the disclosure of sensitive medical data, while the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) requires financial institutions to safeguard customer data and provide data privacy notices.
But these regulations aren’t always enough to protect confidential data against compromise. Both malicious and accidental exposures of highly sensitive data have been making the news for the last decade.
For instance, attackers in 2013 exposed the account information from a shocking 3 billion Yahoo user accounts. In 2017, information on more than 120 million US households was exposed after an Amazon Web Services (AWS) S3 storage bucket was misconfigured. And in 2023, over 37 million T-Mobile customers had their personal information stolen by an attacker.
How can data confidentiality be strengthened?
Physical measures like air gaps, locked doors, and secure company laptops are an important start. It’s also wise to use a secure internet connection and devices with appropriate firewalls, anti-malware systems, and other security measures.
But data confidentiality doesn’t stop there. Data encryption — which uses a key to convert data into secret code — and encrypted communication channels are often used to protect highly sensitive data.
ShardSecure offers an innovative, agentless approach to file-level protection, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive material and ensuring data confidentiality.
Data integrity
The second component of the CIA triad, data integrity ensures that data remains accurate, consistent, and complete through every stage of its lifecycle. Whether it's being stored, retrieved, or modified, data must remain consistent, correct, and whole.
Data integrity encompasses physical integrity measures, which seek to protect data from problems like power outages and hardware failures. It also includes logical integrity measures, which ensure that data remains accessible, unchanged, and error-free.
Some key threats to data integrity include:
- Human error and misconfigurations
- Malware
- Ransomware
- Semantic attacks
- Formatting and syntax errors
- Natural disasters and power outages
Data integrity is particularly important as the worldwide volume of data grows rapidly, with up to 181 zettabytes of data expected to exist by 2025. It’s also a key component of compliance with data protection and privacy regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, and beyond.
How can data integrity be ensured?
Organizations can maintain data integrity by implementing processes to ensure that their data — whether it be data-in-use, data-in-transit, or data-at-rest — remains valid and unchanged by any unauthorized user. These processes should govern actions like data entry, deletion, transfer, and updates. Here are a few key tips:
- Data must be backed up regularly.
- Data access controls must be implemented following the principle of least privilege.
- Data inputs and data transmission must be verified to detect errors.
- Data audit trails must be maintained.
You can also strengthen your data integrity with ShardSecure. Our technology performs multiple data integrity checks to help ensure that critical data at rest stays secure and available. In the event of any unauthorized changes to data, we immediately alert your organization and restore the data transparently and in real-time.
Data availability
The third principle of the CIA triad, data availability, refers to the reliability, accessibility, and timeliness of data. Data availability ensures that you’ll be able to access what you need, at a normal level of performance, whenever you want it.
Poor data availability can cause major interruptions to business continuity. Key threats to data availability include:
- Storage failures. If a physical storage device fails, data will no longer be accessible. This is of particular concern to organizations who use on-prem storage.
- Server and network crashes. When a server or network fails, any data accessed through it will become temporarily unavailable.
- Slow data transfers. Poor data transfer speeds can make data more difficult to access.
- Data compatibility. Data may not be accessible if the environments where it’s being stored and accessed are not compatible with each other.
- Ransomware. Attacks by malicious actors can drastically interfere with data availability, encrypting valuable files and making them inaccessible to authorized users.
- Losing access to cloud storage. In addition to being vulnerable to ransomware, data stored in the cloud can become inaccessible in myriad ways. Lost passwords, accidental deletions, user errors, account suspensions, cloud outages, and even storage provider bankruptcies can all render data unavailable.
How can data availability be improved?
First, data backups can help restore systems quickly in the event of an outage or loss. Backups should be tested from time to time to make sure that the backup and restore process works.
Second, data loss prevention tools may be helpful. These tools, which often come in the form of SaaS platforms that monitor and control access to data, can help mitigate availability risks.
Third, data should be inventoried. This process ensures that your organization knows the different types and amounts of data you have, and it helps inform better data management practices.
Lastly, data should be securely destroyed once it’s no longer needed. Sensitive datasets in particular must be disposed of or securely erased to ensure that their contents cannot be accessed.
ShardSecure offers an additional way to ensure data access with high availability. Each instance of ShardSecure is a virtual cluster that can be run on-premises or in the cloud, and customers can configure two or more virtual clusters for failover. This keeps data available even in the event of cloud provider outages, power failures, server crashes, and other expected downtime.
Upholding the CIA triad with ShardSecure
Our Data Control Platform inherently upholds the CIA triad with strong data confidentiality, multiple data integrity checks, and high availability. Our self-healing data also means that we can rebuild data whenever it’s tampered with, deleted, or compromised.
With this foundation, ShardSecure’s technology is able to offer strong data security and resilience to companies in a wide range of industries, including healthcare, tech, financial services, manufacturing, and more.
Interested in learning more about how ShardSecure can help your organization uphold the CIA triad? Visit our solutions pages, take a look at the detailed white paper on our technology, or schedule a demo today.
Sources
Timeline of the History of Information Security | Saylor
Toward a Better Understanding of “Cybersecurity” | Association for Computing Machinery
The 15 Biggest Data Breaches of the 21st Century | CSO Online
The Top 8 Recent High-Profile Data Breaches from 2023 | Electric
25+ Impressive Big Data Statistics for 2022 | TechJury
Data Integrity Information Security | ISACA Journal
What is Data Integrity in Databases? | Techopedia
Managing Data Availability | University of Delaware
NIST Special Publication 800-88 | National Institute of Standards and Technology